ملف:Free-living amebic infections.png
حجم البروفه دى: 700 × 600 بكسل. الأبعاد التانيه: 280 × 240 بكسل | 560 × 480 بكسل | 896 × 768 بكسل | 1,195 × 1,024 بكسل | 1,365 × 1,170 بكسل.
الصوره الاصليه (1,365 × 1,170 بكسل حجم الفايل: 715 كيلوبايت، نوع MIME: image/png)
تاريخ الفايل
اضغط على الساعه/التاريخ علشان تشوف الفايل زى ما كان فى الوقت ده.
| الساعه / التاريخ | صورة صغيرة | ابعاد | يوزر | تعليق | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| دلوقتي | 09:24، 2 فبراير 2023 |  | 1,365 × 1,170 (715 كيلوبايت) | Materialscientist | https://answersingenesis.org/biology/microbiology/the-genesis-of-brain-eating-amoeba/ |
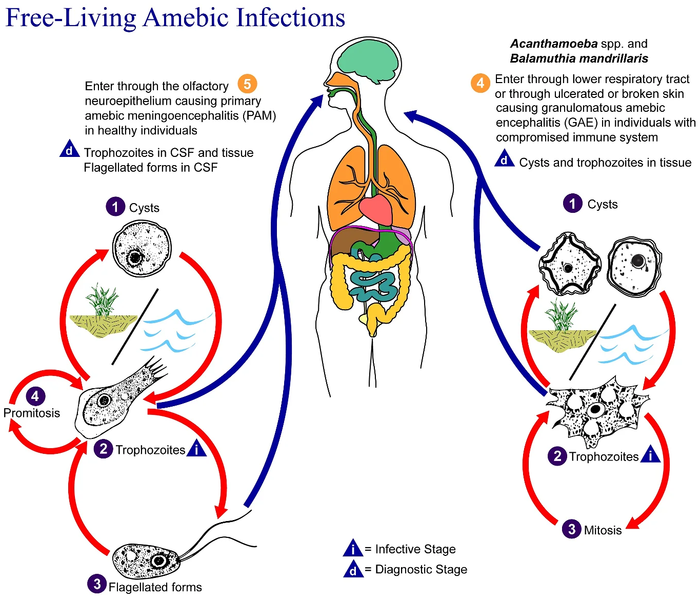
| 06:30، 20 يوليه 2008 |  | 518 × 435 (31 كيلوبايت) | Optigan13 | {{Information |Description={{en|This is an illustration of the life cycle of the parasitic agents responsible for causing “free-living” amebic infections. For a complete description of the life cycle of these parasites, select the link below the image |
استخدام الفايل
مافيش صفحات بتوصل للفايل ده.
استخدام الملف العام
الويكيات التانيه دى بتستخدم الفايل ده:
- الاستخدام ف de.wikibooks.org
- الاستخدام ف en.wiktionary.org
- الاستخدام ف fi.wikipedia.org
- الاستخدام ف fr.wikipedia.org
- الاستخدام ف gl.wikipedia.org
- الاستخدام ف hr.wikipedia.org
- الاستخدام ف is.wikipedia.org
- الاستخدام ف it.wikipedia.org
- الاستخدام ف pl.wikipedia.org
- الاستخدام ف te.wikipedia.org
- الاستخدام ف vi.wikipedia.org
- الاستخدام ف www.wikidata.org
- الاستخدام ف zh.wikipedia.org